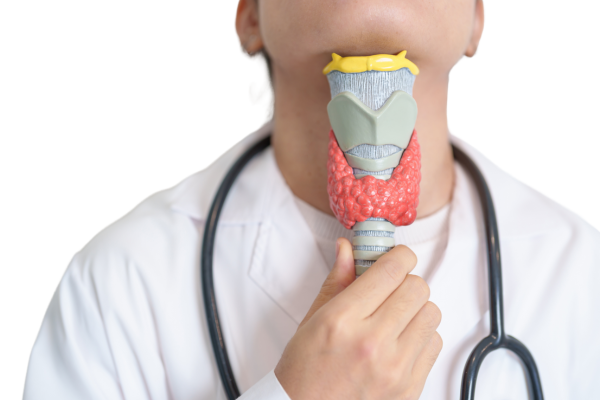
What is Thyroid Treatment?
Thyroid treatment involves medical interventions to manage disorders affecting the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. The thyroid plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and hormone balance by producing thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) hormones. For certain cases, surgical intervention or radioactive iodine therapy may be necessary, particularly in cases of thyroid nodules, goiter, or thyroid cancer. Regular monitoring and medical supervision are essential to ensure effective management and prevent complications.
Thyroid disorders can result in either hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), leading to a range of health complications. Treatment options vary depending on the condition and may include medications, hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, surgery or radioactive iodine therapy.
Causes of Thyroid Disorders:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis – The immune system attacks the thyroid, leading to hypothyroidism.Parasitic infections – Malaria, typhoid, leptospirosis.
- Iodine Deficiency or Excess: Deficiency – The thyroid needs iodine to produce hormones; lack of iodine can cause hypothyroidism and goiter.
- Thyroid Nodules or Tumors: Abnormal growths on the thyroid may overproduce hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism.
- Inflammation of the Thyroid (Thyroiditis): Viral or bacterial infections can cause temporary hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism.
- Congenital Hypothyroidism (Birth Defects): Some babies are born with an underdeveloped or missing thyroid gland, leading to lifelong hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid Nodules or Goiter – Abnormal growths on the thyroid gland can either produce excess thyroid hormones (causing hyperthyroidism) or enlarge the gland, leading to swallowing or breathing difficulties.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders:
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles – Heavy, prolonged periods (hypothyroidism) or lighter, irregular periods (hyperthyroidism).
- Hoarseness or Voice Changes – The thyroid gland's enlargement may cause voice changes or a hoarse throat.
- Difficulty Sleeping (Insomnia) – Trouble falling or staying asleep, especially in hyperthyroidism, due to increased metabolism.
- Weight Gain – Unexplained increase in body weight despite normal diet and activity levels.
- Puffy Face and Swelling – Fluid retention causing facial puffiness and swollen limbs.
- Constipation – Slower digestion leading to infrequent bowel movements.
- Hand Tremors (Shaking Hands) – Involuntary shaking of hands or fingers.
- Increased Sweating and Heat Intolerance – Feeling excessively warm.