What is Insulin Treatment?
Insulin treatment is a medical therapy used to regulate blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows glucose from the bloodstream to enter cells, where it is used for energy. In people with diabetes, either the body does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 Diabetes) or does not use insulin effectively (Type 2 Diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). Insulin therapy helps manage blood glucose by supplementing or replacing the body's natural insulin. It is administered through injections or insulin pumps and comes in different types, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin, depending on individual needs.
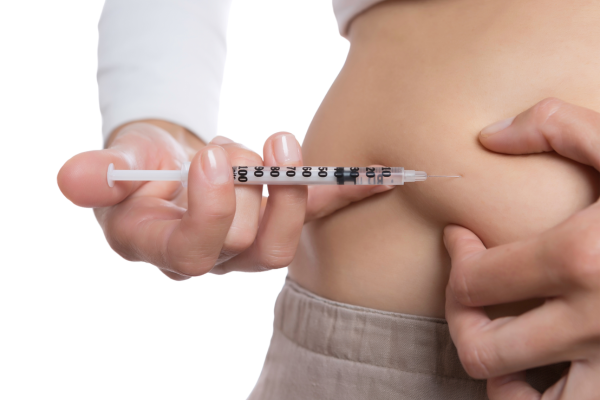

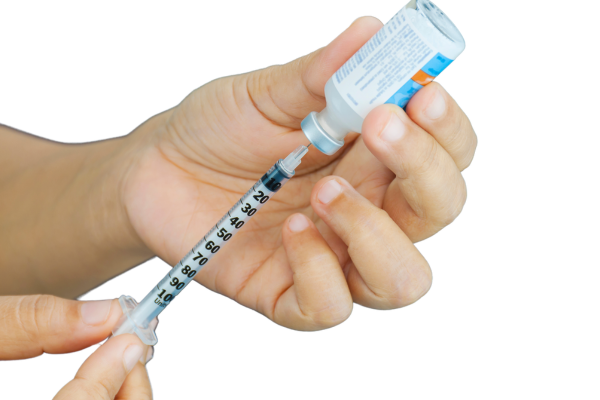
Causes for Needing Insulin Treatment:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells – The immune system mistakenly attacks the beta cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance – The body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, requiring more insulin production.
- Gestational Diabetes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy – Some pregnant women develop insulin resistance, requiring insulin therapy to control blood sugar levels.
- Pancreatic Disorders: Pancreatitis – Inflammation of the pancreas damages insulin-producing cells.
- Steroid-Induced Diabetes: Prolonged corticosteroid use – Steroid medications (e.g., prednisone) can cause high blood sugar levels, leading to the need for insulin therapy.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Insulin Treatment:
- Persistent High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Frequent blood sugar levels above the normal range, even with diet and oral medications.
- Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: Excess glucose in the bloodstream draws water from tissues, leading to dehydration and increased thirst.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite eating normally, the body breaks down muscle and fat for energy due to lack of insulin, leading to unintentional weight loss.
- Extreme Fatigue and Weakness: Cells cannot absorb glucose for energy, leading to persistent tiredness, fatigue, and lack of strength.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can cause fluid imbalances in the eye, leading to vision disturbances and difficulty focusing.